Vol. 25 - Num. 100
Notas clínicas
Indometacina como tratamiento de granuloma eosinófilo multifocal
Casimira Rodríguez Rodrígueza, Pedro Mateos Burguillob
aPediatra. CS Sanchinarro. Madrid. Profesora Asociada de Pediatría. Universidad Alcalá de Henares. Alcalá de Henares. Madrid. España.
bPediatra. CS Jazmín. Madrid. Profesor Asociado de Pediatría. Universidad Alcalá de Henares. Alcalá de Henares. Madrid. España.
Correspondencia: C Rodríguez. Correo electrónico: casimira.rodriguez@salud.madrid.org
Cómo citar este artículo: Rodríguez Rodríguez C, Mateos Burguillo P. Indometacina como tratamiento de granuloma eosinófilo multifocal . Rev Pediatr Aten Primaria. 2023;25:399-404. https://doi.org/10.60147/2bd0715a
Publicado en Internet: 19-12-2023 - Número de visitas: 8162
Resumen
Granuloma eosinófilo es la variante más frecuente de histiocitosis de células de Langerhans. La mayoría de las lesiones ocurren en cráneo, costillas, columna vertebral o huesos largos, y pueden ser únicas o múltiples. El tratamiento depende del lugar de la afectación y del número de lesiones. Las opciones terapéuticas incluyen un agente único con prednisona, la combinación de vinblastina y prednisona, curetaje de las lesiones óseas o instilación intralesional de esteroides. Indometacina parece ser efectiva como tratamiento de lesiones de histiocitosis de células de Langerhans del hueso en niños y es bien tolerada. Presentamos el caso de un paciente varón de 4 años de edad con afectación de 2 huesos del cuerpo, cráneo y vértebra, tratado con curetaje de la lesión craneal e indometacina oral durante 19 meses, con completa curación de las lesiones y sin recurrencia 4 meses después de suspenderla. Concluimos que indometacina parece ser efectiva en el tratamiento de lesiones óseas de histiocitosis de células de Langerhans en niños, evitando otras terapias más agresivas.
Palabras clave
● Granuloma eosinófilo ● Histiocitosis de células de Langerhans ● Indometacina ● NiñosINTRODUCCIÓN
La histiocitosis de células de Langerhans (HCL) es un grupo de procesos similares histológicamente caracterizados por infiltración de los tejidos por células de la línea monocito-macrófago, células que normalmente tienen un importante papel en el sistema inmune. La patogénesis no se conoce completamente, y algunos estudios apuntan sobre un posible origen viral o inmune1.
Las formas clínicas varían de generalizadas y fulminantes a localizadas y curables2.
La forma aislada del hueso se denomina granuloma eosinófilo (GE), es la más frecuente manifestación de HCL (60-80%), y una de las variantes más leves de la enfermedad. Se considera una forma de tumor benigno, ocupando menos del 1% de todos los tumores óseos2. Fue descrito por primera vez en 1940 por Lichtenstein y Jaffe. En el 80% de los casos afecta a niños y adolescentes3 con una incidencia de 4 a 5 casos por millón de niños por debajo de los 15 años4. Hay pocos casos reportados en la misma familia y el modelo de herencia no se conoce bien5.
Se puede manifestar como una lesión solitaria (monostótica o unifocal) (80%), que es más frecuente en niños por encima de 5 años de edad, o múltiple (poliostótica o multifocal). Los huesos más frecuentemente afectados son el cráneo, seguido de costillas, pelvis, huesos largos, vértebras y mandíbula6. A nivel de columna vertebral, la torácica se ve más afectada en niños y la cervical en adultos.
La presentación clínica depende del hueso afectado, siendo lo más frecuente dolor y tumefacción local, y lo más raro, fracturas patológicas. En columna vertebral puede haber dolor del dorso y rigidez con cambios posturales, y si la extensión es mayor puede haber daño neurológico. La analítica sanguínea es habitualmente normal.
En las pruebas de imagen: radiografía (Rx), tomografía axial computarizada (TAC) y resonancia magnética nuclear (RMN), se presenta una apariencia lítica con o sin esclerosis en los márgenes7. Las lesiones espinales afectan sobre todo al cuerpo vertebral y se muestran como lesión lítica o anormal aplanamiento del mismo con edema perilesional.
Es necesaria la confirmación histológica realizada por aspiración con aguja fina o biopsia de la masa, donde se observan a microscopía electrónica los gránulos de Birbeck intracelulares, así como inmunohistoquímica para descartar la mutación BRAF8.
Diferentes aproximaciones se han hecho para tratar lesiones óseas en niños: observación, inyecciones de esteroides9, cirugía, quimioterapia y radioterapia. Recientemente se está haciendo una aproximación terapéutica que conlleve menos complicaciones, como indometacina. Presentamos el caso de un paciente varón de 4 años de edad con afectación ósea del cráneo y vértebra dorsal tratado con indometacina y con respuesta favorable.
CASO CLÍNICO
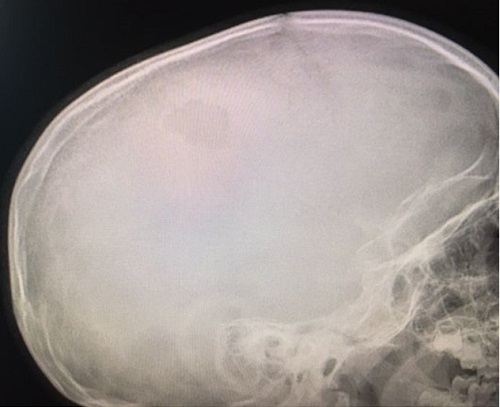
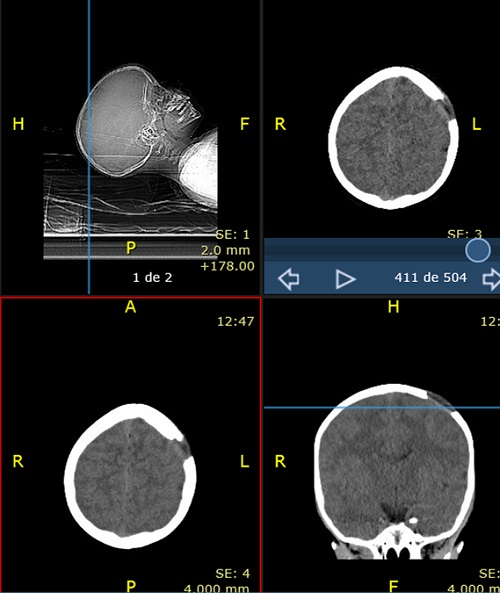
Paciente de 4 años que acude con su madre a consulta por bultoma en cuero cabelludo descubierto de forma casual 7 días antes, sin relación con antecedente traumático y con dolor a la palpación. Desde entonces presenta despertares nocturnos con irritabilidad, que mejoran con analgésicos. Antecedentes familiares y personales sin interés. Desarrollo madurativo normal. Vacunas adecuadas para su edad. No alergias conocidas. El paciente presenta muy buen estado general, apirético y con exploración normal, tanto somática como neurológica, salvo tumoración de consistencia blanda en región parietal izquierda de 2,5-3 cm de diámetro, dolorosa a la palpación. Se deriva al hospital de referencia para pruebas de imagen. La Rx de cráneo muestra una lesión osteolítica en sacabocados, posiblemente compatible con GE (Figura 1). Rx de tórax, serie ósea y ecografía abdominal normales. TAC craneal evidencia los mismos signos (Figura 2). La RMN detecta una lesión única intraósea expansiva parietal izquierda, que atraviesa la tabla ósea externa e interna con mínimo engrosamiento, e hipercaptación de la duramadre subyacente, sugerente de GE como primera posibilidad radiológica. Hemograma y bioquímica dentro de la normalidad.
Se realiza craniectomía con resección de la lesión, obteniéndose un disco de diploe óseo de 35 x 34 x 6 mm y cuyo examen microscópico es compatible con HCL (GE) con resultado inmunohistoquímico frente a BRAF V600E (anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) Mouse Monoclonal Primary. Antinodo. Ventana. Roche): positivo.
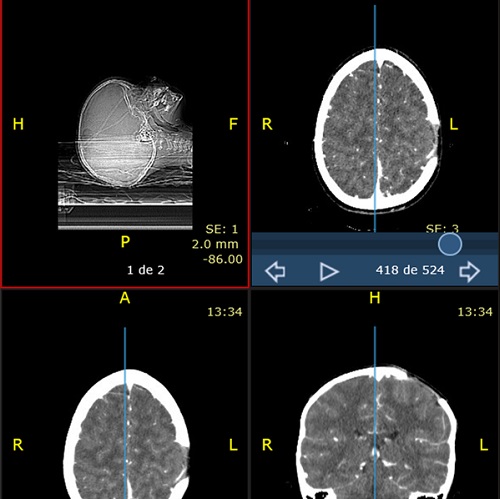
El paciente permanece asintomático hasta un mes después, cuando se objetiva un nuevo bultoma doloroso al tacto, medial a la lesión previa, realizándose nuevo TAC cerebral y confirmándose una lesión lítica de nueva aparición en la región parietal parasagital izquierda, medial a la lesión anterior, sin componente de partes blandas (Figura 3).
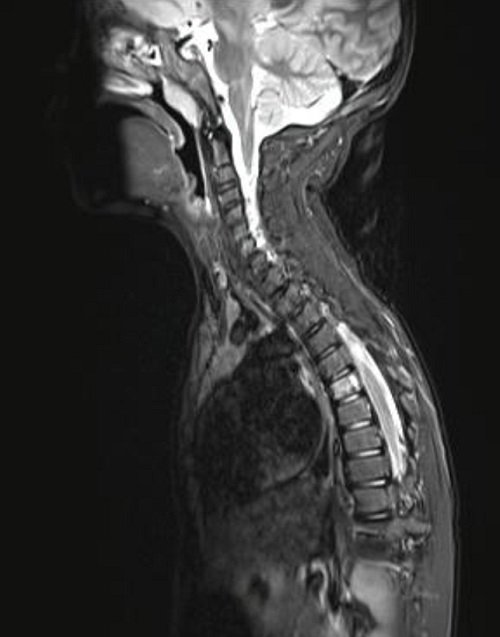
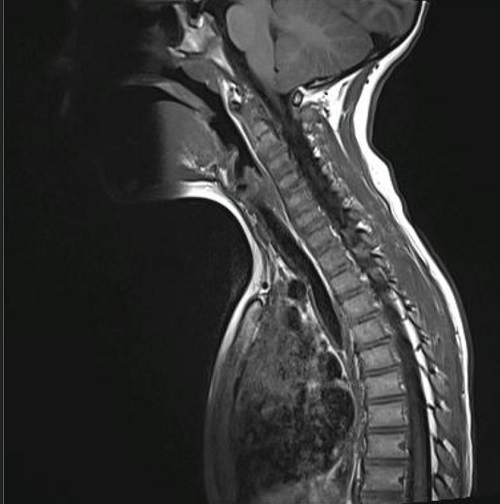
Dos meses después de la intervención quirúrgica, por algias en región dorsal, se realiza tomografía por emisión de positrones (PET/TAC) donde se aprecian las 2 lesiones ya conocidas en hueso parietal izquierdo y se detecta un foco hipermetabólico con gran intensidad de captación en lesión lítica situada en hemicuerpo izquierdo de D6. No se encuentran otros hallazgos en el resto del esqueleto ni en partes blandas, vísceras o ganglios linfáticos. La RMN confirma el hallazgo y se aprecia una lesión en D6, inespecífica, osteolítica, con algunos focos de esclerosis periféricos, compatible con hemangioma vertebral sin poder descartar GE en el contexto del paciente. La presencia de edema óseo perilesional iría a favor de GE (Figura 4).
El Servicio de Hemato-Oncología del hospital de referencia, junto con los padres, decide iniciar tratamiento con indometacina, a 2 mg/kg/día. Desde entonces, el paciente se mantiene asintomático y en los controles de imagen periódicos se va notando reducción de las lesiones. Diecinueve meses después del inicio del tratamiento realizan nueva RMN que muestra ausencia de resto o recidiva de su patología de base: defecto óseo parietal izquierdo ya conocido y estable. Práctica resolución de la lesión en la vertiente izquierda del cuerpo de D6 (Figura 5). Ante estos hallazgos se decide retirar el tratamiento, permaneciendo asintomático cuatro meses después de la suspensión del mismo.
DISCUSIÓN
La HCL es una rara enfermedad que se manifiesta con más frecuencia por una única o múltiple lesión ósea osteolítica con infiltrado de histiocitos en la biopsia. En general, el tratamiento de lesión solitaria típica y asintomática es conservador9, ya que presenta buen pronóstico y puede resolverse espontáneamente. Sin embargo, si la lesión es sintomática, es preferible hacer biopsia para confirmar diagnóstico histológico y posterior tratamiento, aunque muchas lesiones mejoran después de la biopsia.
Presentamos el caso de un paciente de 4 años con dos lesiones craneales y una en vértebra dorsal, diagnosticadas por sintomatología local sin deficiencias neurológicas. El primer tratamiento realizado fue craniectomía con resección de la primera lesión, donde se confirma GE por estudio histológico y cuyo resultado inmunohistoquímico demuestra que es portador de mutación BRAF V600E.
La mejor aproximación terapéutica sería la que asegurara una curación con poca posibilidad de complicaciones. Varias opciones se han barajado para el tratamiento de GE óseo: escisión local y curetaje con o sin injerto, metilprednisolona intralesional, radioterapia y quimioterapia. Esta última no se recomienda en GE solitario y debería ser reservada en afectación sistémica10.
Se debate sobre si GE es un proceso reactivo o neoplásico. La proliferación de células de Langerhans puede ser inducida por una infección viral (virus de Epstein Barr, herpes virus 6) o bacterias, o por una alteración genética. Todo ello generaría una disfunción del sistema inmune1, con incremento de citoquinas, tal como IL-1 e IL-10, con posible implicación de prostaglandinas en la patogénesis. En este sentido, la metilprednisolona intralesional, al inhibir las prostaglandinas, mejoraría el dolor y curaría la lesión ósea10 El uso de indometacina oral en el tratamiento de distintas formas de HCL ha sido reportado anteriormente11. Indometacina es un fármaco antinflamatorio no esteroideo que inhibe la ciclooxigenasa y, de esta forma, bloquea la vía del ácido araquidónico y prostaglandinas, actuando sobre la patogenia de la enfermedad. Indometacina oral a dosis de 1-2 mg/kg/día durante 6-12 meses se considera entre los menos tóxicos y más eficaces tratamientos, con función analgésica, además de tener capacidad para revertir la enfermedad en niños con HCL ósea, como primera terapia o tras reactivación, con mínimos efectos secundarios11,12. Cuando se ha comparado en lesiones óseas con otras modalidades terapéuticas más agresivas, como la quimioterapia, se consigue curación completa y recuperación funcional en similar periodo de tiempo, sin recurrencias locales13.
Nuestro paciente presentaba afectación multifocal y fue tratado con curetaje de la lesión craneal además de indometacina a dosis de 2 mg/kg/día durante 19 meses, sin efectos secundarios, mostrando una primera línea de tratamiento farmacológico beneficiosa, con progresiva remisión de las lesiones, hasta la completa desaparición de las mismas. Estos resultados confirman la eficacia de indometacina en un paciente con HCL ósea multifocal, especialmente como primera línea de tratamiento.
En el estudio inmunohistoquímico de la biopsia se encontró mutación BRAF y, aunque en algunos estudios se ha visto correlación con pobre respuesta al tratamiento de primera linea14, en otros estudios no se ha demostrado diferencia en el pronóstico9.
Aunque el tiempo de evolución sin tratamiento es escaso (4 meses), la resolución de las lesiones óseas y la falta de sintomatología nos permite pensar que la curación sea permanente.
CONCLUSIONES
El granuloma eosinófilo afecta principalmente a la población infantil y adolescente, es de carácter benigno, pero precisa de un correcto diagnóstico para una intervención terapéutica temprana. La historia clínica del paciente, así como las imágenes radiológicas sugerentes y la comprobación histológica e inmunohistoquímica lleva a una primera aproximación terapéutica, indometacina oral, que ha demostrado su eficacia, con resolución de las lesiones, que ha sido bien tolerada y sin necesidad, hasta la actualidad, de recurrir a terapias más agresivas.
CONFLICTO DE INTERESES
Los autores declaran no presentar conflictos de intereses en relación con la preparación y publicación de este artículo. Este trabajo no ha recibido financiación.
RESPONSABILIDAD DE LOS AUTORES
Todos los autores han contribuido de forma equivalente en la elaboración del manuscrito publicado. Los autores han remitido un formulario de consentimiento de los padres/tutores para publicar información de su hijo/a.
ABREVIATURAS
GE: granuloma eosinófilo · HCL: histiocitosis de células de Langerhans · PET/TAC: tomografía por emisión de positrones · RMN: resonancia magnética nuclear · Rx: radiografía · TAC: tomografía axial computarizada.
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
- Azouz EM, Saigal G, Rodriguez MM, Podda A. Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis: pathology, imaging and treatment of skeletal involvement. Pediatr Radiol 2005;35(2):103-15. https://org/10.1007/s00247-004-1262-0
- Chadha M, Agarwal A, Agarwal N, Singh MK. Solitary eosinophilic granuloma of the radius: An unusual differential diagnosis. Acta Orthop Belg 2007;73(3):413-17.
- Greenlee JD, Fenoy AJ, Donovan KA, Menezes AH. Eosinophilic granuloma in the pediatric spine. Pediatr Neurosurg 2007;43(4):285-92. https://doi.org/10.1159/000103308
- Allen CE, Ladisch S, McClain KL. How I treat Langerhans cell histiocytosis. 2015;126(1):26-35. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-12-569301
- Aricò M, Nichols K, Whitlock JA, Arceci R, Haupt R, Mittler U, et al. Familial clustering of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Br J Haematol 1999;107:883. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.1999.01777.x
- Cochrane LA, Prince M, Clarke K. Langerhans' cell histiocytosis in the paediatric population: presentation and treatment of head and neck manifestations. J Otolaryngol. 2003;32(1):33-7.
- Khung S, Budzik JF, Amzallag Bellenger E, Lambilliote A, Ares GS, Cotten A, et al. Skeletal involvement in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Insights Imaging. 2013;4(5):569-79. https://org/10.1007/s13244-013-0271-7
- Badalian Very G, Vergilio JA, Degar BA, MacConaill LE, Brandner B, Calicchio ML, et al. Recurrent BRAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. 2010;116(11):1919-23. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-04-279083
- Capanna R, Springfield DS, Ruggieri P, Biagini R, Picci P, Bacci G, et al. Direct cortisone injection in eosinophilic granuloma of bone: a preliminary report on 11 patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 1985;5(3):339-42. https://doi.org/10.1097/01241398-198505000-00016
- Mavrogenis AF, Abati CN, Bosco G, Ruggieri P. Intralesional methylprednisolone for painful solitary eosinophilic granuloma of the appendicular skeleton in children. J Pediatr Orthop.2012; 32(4):416-22. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182561153
- De Benedittis D, Mohamed S, Rizzo I, Santopietro M, Palumbo G, Cardarelli I, et al. Indomethacin is an effective treatment in adults and children with bone Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH). Br J Haematol, 2020;191:e109-e113. http://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17067
- Han I, Suh ES, Cho HS, Han J, Kim HS. Management of eosinophilic granuloma occurring in the apendicular skeleton in children. Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery. 2009;1:63-7. http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2009.1.2.63
- Braier J, Rosso D, Pollono D, Rey G, Lagomarsino E, Latella A, et al. Symptomatic bone Langerhans cell histiocytosis treated at diagnosis or after reactivation with indomethacin alone. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014;36(5):280-4. http://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0000000000000165001
- Héritier S, Emile JF, Barkaoui MA, Thomas C, Fraitag S, Boudjemaa S, et al. BRAF Mutation Correlates with High-Risk Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis and Increased Resistance to First-Line Therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:3023-30. http://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.65.9508