Vol. 24 - Num. 93
Originales
Riesgo de contagio por COVID-19 en función del tipo de contacto y de la renta familiar
Álvaro Baeta Ruiza, José M.ª Mengual Gilb, Beatriz Ortega Aguilarc, Sonia Duce Camachod, Nuria García Sánchezb, Neelam Mithumal Dadlani Dadlani a, Paloma del Carmen Jolín Garcíab
aMIR-Pediatría. Hospital Clínico Universitario Lozano Blesa. Zaragoza. España.
bPediatra. CS Delicias Sur. Zaragoza. España.
cMIR-Medicina de Familia. Hospital Clínico Universitario Lozano Blesa. Zaragoza. España.
dEnfermera. CS Delicias Sur. Zaragoza. España.
Correspondencia: A Baeta . Correo electrónico: a.baeta11@gmail.com
Cómo citar este artículo: Baeta Ruiz A, Mengual Gil JM, Ortega Aguilar B, Duce Camacho S, García Sánchez N, Dadlani Dadlani NM, et al. Riesgo de contagio por COVID-19 en función del tipo de contacto y de la renta familiar. Rev Pediatr Aten Primaria. 2022;24:31-7.
Publicado en Internet: 28-03-2022 - Número de visitas: 13933
Resumen
Introducción: tras una segunda oleada de la pandemia COVID-19 en Zaragoza, se estudian los contactos estrechos con pacientes con COVID-19, con la finalidad de valorar el riesgo de infección tras exposición en función del paciente índice, adulto o niño, y la renta familiar.
Material y métodos: se realiza un estudio descriptivo de todos los pacientes pediátricos que han tenido contacto con pacientes con COVID-19 en el centro de salud de Delicias Sur de Zaragoza entre los meses de julio y agosto de 2020 y se valora la aparición de síntomas, consultas en servicio de urgencias, realización de pruebas complementarias, contacto estrecho con adulto o con niño y la renta familiar.
Resultados: un total de 292 pacientes fueron contacto estrecho con pacientes con COVID-19, de los cuales 128 fueron positivos para la PCR de SARS-CoV-2. Al analizar el tipo de contacto, se encontró que un 10,94% había mantenido contacto estrecho con un niño y un 89,06% con un adulto. El riesgo de contagio tras sufrir contacto con un niño positivo fue del 34,15%, mientras que, tras contacto con un adulto positivo, el riesgo fue del 45,78%. Asimismo, el riesgo de contagio entre las rentas inferiores a 18 000 € fue de 47,9 frente al 27,6% de aquellos pacientes con rentas superiores a 18 000 €.
Conclusiones: el riesgo de contagio de COVID-19 es mayor cuando el contacto estrecho es con un adulto y cuando el nivel de renta familiar es inferior.
Palabras clave
● COVID-19 ● Renta familiar ● SARS-CoV-2 ● Seguimiento de contactos ● Transmisión de enfermedades infecciosasINTRODUCCIÓN
La COVID-19 es la enfermedad infecciosa causada por el coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 que fue detectada inicialmente en China y que rápidamente se extendió a todos los países. Este virus causa una infección respiratoria que se puede propagar de persona a persona a través de las gotículas que salen despedidas de la nariz o la boca de una persona infectada al toser, estornudar o hablar; por el contacto con superficies contaminadas por el virus o mediante aerosoles que pueden permanecer suspendidos en al aire incluso varias horas. Algunos autores afirman que la transmisión a través de aerosoles podría suponer hasta el 75% de los contagios1.
En cuanto a la población pediátrica se ha observado que los casos positivos suelen ser secundarios a contacto con un adulto positivo, siendo muy importante la transmisión intrafamiliar. Además, los niños con infección por coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 suelen tener una clínica más leve que los adultos y suelen desarrollar menor número de síntomas2,3.
Desde la aparición de los primeros casos de infección por SARS-CoV-2 en China, se planteó cómo podía afectar el virus a la población pediátrica y cómo podían estar implicados los niños en la cadena de transmisión. Esta preocupación llevó a tomar medidas extraordinarias en nuestro país, como el cierre de aulas y el confinamiento en los domicilios durante aproximadamente 70 días, finalizando el 20 de junio de 2020. El periodo de nuestro estudio incluye los meses de julio y agosto, cuando no había restricciones de movilidad ni confinamiento en domicilios y coincidía con el periodo de vacaciones escolares de nuestra población pediátrica.
El objetivo principal del estudio fue valorar si los pacientes pediátricos de nuestra área se habían contagiado tras mantener contacto estrecho con un adulto con COVID-19 o con un niño con COVID-19 y valorar el riesgo de contagio en función de las rentas familiares valoradas por medio del código de aportación farmacéutica de la Tarjeta Sanitaria Individual (TSI). Como objetivos secundarios, se estudiaron la aparición de síntomas entre los pacientes con COVID-19 diagnosticado, la clase de síntomas presentados, consultas en el servicio de urgencias, realización de pruebas complementarias y la necesidad de ingreso hospitalario.
MATERIAL Y MÉTODOS
Estudio retrospectivo descriptivo a través de la historia clínica electrónica de pacientes en el centro de salud Delicias Sur de Zaragoza (España). Se incluyeron aquellos pacientes que fueron codificados en el programa OMI de historia electrónica con los códigos A77 y A23 como contacto de enfermedad infecciosa o como infección por COVID-19 confirmada.
El periodo de estudio fue de dos meses (julio y agosto de 2020) y se incluyeron los niños a partir de un mes de edad hasta los 18 años.
La reacción en cadena de la polimerasa (PCR) para SARS-CoV-2 se consideró como gold standard para establecer el diagnóstico de COVID-19.
Se considera contacto estrecho a aquellos pacientes que han estado expuestos a un paciente con COVID-19 a menos de 1,5 metros de distancia durante más de 15 minutos y sin mascarilla.
Los criterios de exclusión de pacientes para este estudio fueron: menores de 1 mes, mayores de 18 años, no realización de PCR nasofaríngea para SARS-CoV-2 e imposibilidad para identificar el contacto del paciente independientemente del resultado de la PCR.
Se recogió como variable principal el resultado de la PCR de SARS-CoV-2. Las variables secundarias incluidas para el estudio fueron edad, presencia de síntomas (fiebre, tos, rinitis, etc.), consultas en el servicio de urgencias del hospital de referencia, necesidad de realizar pruebas complementarias, necesidad de ingreso hospitalario, contacto con adulto con COVID-19 o niño con COVID-19 y la tasa de ingresos de la familia valorada por medio del código TSI de aportación farmacéutica que se determina en función del nivel de renta y de la situación sociolaboral de los pacientes, por lo que es un indicador indirecto del nivel de ingresos: TSI 001: renta de integración social, parados sin subsidio y pensiones no contributivas; TSI 002: pensionistas; TSI 003: activos con rentas inferiores a 18 000 € anuales; TSI 004: activos con rentas comprendidas entre 18 000 € y 100 000 € anuales; TSI 005: activos con rentas superiores a 100 000 € anuales; TSI 006: mutualistas y clases pasivas (funcionariado del Estado, Instituto Social de las Fuerzas Armadas y Mutualidad General Judicial).
En el análisis descriptivo de los datos se calcularon las medidas de tendencia central y de dispersión (media, mediana y desviación típica) para la edad de la muestra, mientras que, en el caso de las variables cualitativas, los datos se expresaron en valores de frecuencia absolutas y porcentajes. Posteriormente se comparan las diferencias obtenidas mediante el estadístico χ2 estableciendo un valor de significación de p <0,05.
RESULTADOS
Inicialmente, 300 pacientes tenían asignados los códigos OMI requeridos para el estudio, de ellos ocho cumplían criterios de exclusión, por lo que el número final depurado para el estudio fue de 292. Los 292 pacientes fueron contacto estrecho de pacientes con infección por coronavirus. La media de edad de la muestra fue de 8,53 años de edad, una mediana de 9 años, una moda de 14 años y una desviación típica de 5,05. De los 292 pacientes, 139 son mujeres (un 48%) y 153 hombres (52%).
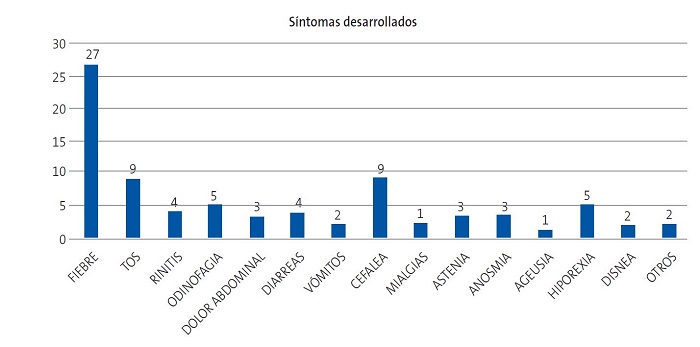
A todos los pacientes se les realizó una PCR diagnóstica para el coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, siendo positiva en 128 niños, es decir, el 43,84% de la población que se estudió. Entre los pacientes que fueron positivos para la PCR de SARS-CoV-2, un 36,72% (47 pacientes) presentó algún tipo de síntoma, mientras que un 63,28% (81 pacientes) se mantuvo asintomático. Entre los 47 pacientes sintomáticos, con PCR de SARS-CoV-2 positiva, se identificaron hasta 15 síntomas diferentes, de ellos, el más frecuente fue la fiebre (27 pacientes), seguido de la tos (9 pacientes) y de la cefalea (9 pacientes) (Fig. 1). De todos los pacientes sintomáticos del estudio (60 pacientes), el 21,67% (13 pacientes) fueron negativos para la PCR de SARS-CoV-2 mientras que el 78,33% (47 pacientes) fueron positivos para la PCR SARS-CoV-2.
Entre los pacientes con sintomatología, nueve (19,15%) pacientes requirieron ser valorados en el servicio de urgencias, siendo todos ellos positivos para COVID-19. En estos nueve pacientes, solo se realizaron pruebas complementarias en tres (radiografía de tórax). Ninguno de nuestros pacientes requirió ingreso hospitalario.
| Figura 1. Representación de los diferentes síntomas desarrollados entre los pacientes que fueron positivos para la PCR de SARS-CoV-2. Se incluyeron 15 síntomas. Otros de los síntomas detectados fueron irritabilidad y dolor torácico |
|---|
 |

Uno de los intereses principales de nuestro estudio fue valorar si el contacto estrecho había sido con un adulto o con un niño con COVID-19. De todos los pacientes de la muestra, un 13,35% (39 pacientes) había mantenido contacto estrecho con un niño mientras que, en el 83,90% (245 pacientes), el contacto había sido con un adulto. En un 2,75% de los casos (ocho pacientes), el contacto había sido doble, con un adulto y con un niño al mismo tiempo. De los pacientes que fueron positivos para la PCR de SARS-CoV-2, un 10,94% (14 pacientes) mantuvieron contacto con un niño mientras que el 89,06% (114 pacientes) mantuvieron contacto con un adulto.
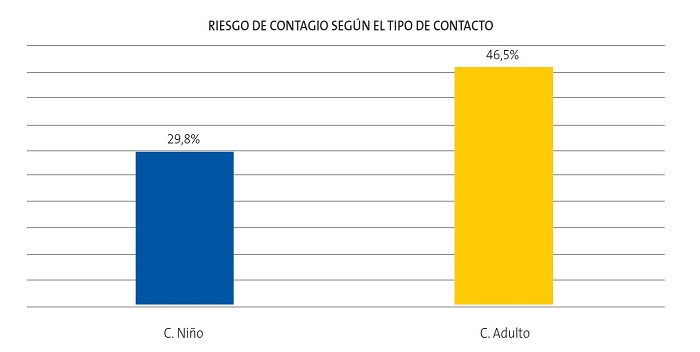
El riesgo de contagio de COVID-19, es decir, la probabilidad de tener una PCR para SARS-CoV-2 positiva tras mantener contacto estrecho con un niño COVID-19 positivo fue del 29,8%, mientras que la probabilidad de tener una PCR para SARS-CoV-2 positiva tras mantener contacto estrecho con un adulto positivo fue del 46,5% (Fig. 2), siendo estos resultados estadísticamente significativos. Asimismo, el 70,2% de los niños que mantuvieron contacto con un niño COVID-19 positivo y el 53,5% de los niños que mantuvieron contacto con un adulto COVID-19 positivo no se infectaron.
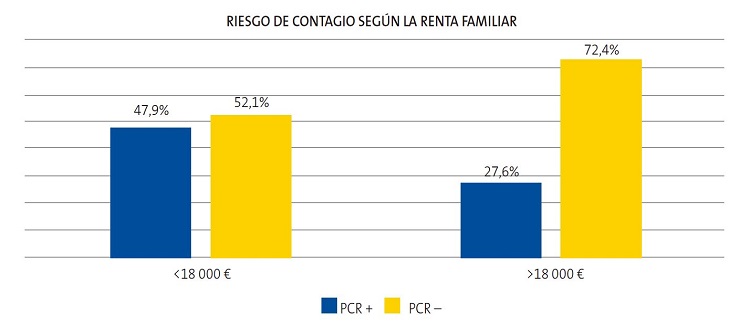
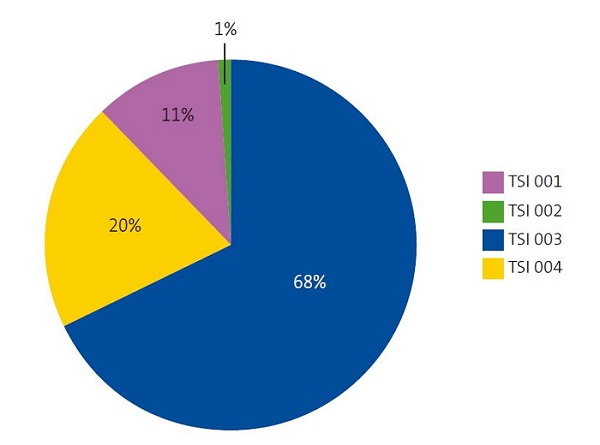
Se estudia la muestra de nuestros pacientes en función de la renta familiar según el código TSI de aportación farmacéutica. Un 80% de la población del centro de salud de Delicias Sur tenía TSI 003 o inferior, lo que implica rentas anuales inferiores a 18 000 €, mientras que el 20% tenía TSI 004, implicando una renta entre 18 000 € y 100 000 € anuales. Ninguno de nuestros pacientes tenía TSI 005 (rentas superiores a 100 000 € anuales) (Fig. 3). Los pacientes con rentas anuales inferiores a 18 000 € que tuvieron contacto estrecho con pacientes con COVID-19 fueron positivos para la PCR de SARS-CoV-2 en un 47,9% (112 pacientes), mientras que el 52,1% (122 pacientes) fueron negativos. En cuanto a los pacientes con rentas anuales superiores a 18 000 € que habían mantenido contacto estrecho con pacientes con COVID-19, el 27,6% (16 pacientes) fueron positivos para la PCR de SARS-CoV-2, mientras que el 72,4% (42 pacientes) fueron negativos (Fig. 4), siendo estos resultados estadísticamente significativos.
| Figura 3. Distribución del total de la muestra (292 pacientes) en función de la renta familiar valorada mediante el código TSI del copago farmacéutico |
|---|
 |

DISCUSIÓN
La fortaleza de nuestro estudio se basa en que se recogieron todos los niños con COVID-19 durante el periodo de estudio de nuestra zona básica de salud (ZBS), circunstancia que disminuye el sesgo de selección de la muestra.
La principal limitación es que la recogida de información ha sido retrospectiva, las encuestas epidemiológicas y el sistema informático usados para recoger los datos no fueron diseñados específicamente para este estudio. La dificultad de comunicación de la población inmigrante que en nuestra ZBS representa un elevado porcentaje también se debe tener en cuenta en este apartado.
Nuestro estudio muestra cómo los niños tienen menos riesgo de presentar una PCR para SARS-CoV-2 positiva si se exponen a un niño con la infección que si lo hacen a un adulto. Además de suponer que los niños tienen por sí mismos una menor capacidad de contagio4, debemos tener en cuenta otros factores: el periodo de realización del estudio fueron los meses de julio y agosto de 2020, se trata del periodo vacacional de colegios e institutos, en el que los pacientes pediátricos pasan más tiempo con sus familiares en los domicilios y los contactos con pacientes de su misma edad suelen ser más frecuentes en actividades de ocio realizadas en espacios al aire libre. Asimismo, al tratarse de los meses de verano, el clima en la ciudad de Zaragoza es cálido y seco, con mayor número de horas al día de radiación ultravioleta, factores que podrían disminuir la transmisibilidad del virus, si bien no existe bibliografía suficiente para corroborarlo5. En el estudio de T. C. Jones6 se estudia la posibilidad de que existan diferentes cargas virales en función de la edad de los pacientes positivos para la PCR de SARS-CoV-2, pero no se obtuvieron diferencias estadísticamente significativas. Tampoco existe bibliografía suficiente acerca de la posibilidad de que los pacientes adultos, por ser más sintomáticos que los pediátricos, puedan ser mayores transmisores de la enfermedad.
La muestra se compone de pacientes recogidos como contacto estrecho de pacientes con COVID-19 del centro de salud de Delicias Sur. El barrio de Delicias en Zaragoza es el barrio más poblado y con mayor densidad de población de la ciudad, así como el que tiene mayor número de población extranjera. La renta media por hogar en el barrio de Delicias es de 27 000 € anuales con una renta individual media de 10 280 € anuales, ambas por debajo de la media de la ciudad de Zaragoza7.
Otra posible limitación es el uso del TSI como indicador de renta familiar, dado que son datos orientativos y no exactos de la renta familiar anual y los rangos que incluye cada TSI son muy amplios, especialmente el TSI 004, incluyendo rentas entre 18 000 € y 100 000 € anuales. En cuanto a nuestra muestra, el 80% de los pacientes tenía rentas familiares inferiores a 18 000 €.
El riesgo de contagio tras exposición con un paciente con COVID-19 es mayor entre los pacientes con rentas familiares inferiores a 18 000 € que entre aquellos con rentas superiores. Las posibles causas de dichas diferencias podrían ser la dificultad de aislamiento domiciliario de los pacientes con rentas inferiores, que habitualmente viven en domicilios más pequeños con menor número de habitaciones, mayor número de convivientes y varios núcleos familiares diferentes habitando en el mismo domicilio.
CONCLUSIONES
Los pacientes pediátricos de nuestra muestra con PCR SARS-CoV-2 positiva se mantuvieron asintomáticos en el 63,28% de los casos. Entre los sintomáticos, todos los pacientes presentaron síntomas leves, siendo el síntoma más frecuente la fiebre, seguido de la tos y la cefalea en preadolescentes.
Los pacientes de nuestro estudio, niños que fueron contacto estrecho de un paciente COVID-19 positivo, tenían un mayor riesgo de contagio de COVID-19 si el contacto era con un adulto que si lo era con un niño. Asimismo, existe un mayor riesgo de contagio tras contacto estrecho en pacientes con rentas familiares anuales inferiores a 18 000 € frente a pacientes con rentas familiares anuales superiores a 18 000 €. Los niños de nuestra muestra tenían aproximadamente 1,5 veces más probabilidades de contagio si se exponían a un adulto que si lo hacían a un niño y 1,5 más probabilidades de contagio si la renta familiar era inferior a 18 000 €, ambas probabilidades calculadas de forma independiente.
CONFLICTOS DE INTERÉS
Los autores declaran no presentar conflictos de intereses en relación con la preparación y publicación de este artículo. No ha existido financiación para la realización del estudio.
Todos los autores contribuyeron a la realización del estudio y aprueban el artículo enviado. BOA y SDC se encargaron de la recogida de datos y del apartado de introducción. PCJG y NMDD se encargaron de los apartados de discusión y conclusiones. NGS, JMMG y ÁBR se encargaron del diseño del estudio y apartados de material y métodos y resultados.
ABREVIATURAS
PCR: reacción en cadena de la polimerasa · TSI: tarjeta sanitaria individual · ZBS: zona básica de salud.
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
- Anderson EL, Turnham P, Griffin JR, Clarke CC. Consideration of the Aerosol Transmission for COVID-19 and Public Health. Risk Anal. 2020;40:902-7.
- Balasubramanian S, Rao NM, Goenka A, Roderick M, Ramanan AV. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Children - What We Know So Far and What We Do Not. Indian Pediatr. 2020;57:435-42.
- Laws RL, Chancey RJ, Rabold EM, Chu VT, Lewis N, Fajans M, et al. Symptoms and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Among Children - Utah and Wisconsin, March-May 2020. Indian Pediatr. 2020;57:435-42.
- Fiel Ozores A, González Durán ML, Novoa Carballal R, Portugués de la Red MM, Fernández Pinilla I, Julio Cabrera Alvargonzález J, et al. Clínica diferencial en niños infectados por SARS-CoV-2, trazabilidad de contactos y rentabilidad de pruebas diagnósticas: estudio observacional transversal. An Pediatr. 2021;94:318-26.
- Paraskevis D, Kostaki EG, Nikiforos A, Thomaidis NS, Cartalis C, Tsiodras S, et al. A review of the impact of weather and climate variables to COVID-19: In the absence of public health measures high temperatures cannot probably mitigate outbreaks. Sci Total Environ. 2021;768:144578.
- Jones TC, Biele G, Muhlemann B, Veith T, Schneider J, Beheim-Schwarzbach J, et al. Estimating infectiousness throughout SARS-CoV-2 infection course. Science. 2021;373:eabi5273.
- Observatorio Urbano de Zaragoza y su Entorno. Zaragoza en datos. Informe global sobre la ciudad y sus distritos. En: Ebropolis [en línea] [consultado el 07/06/2021]. Disponible en: www.ebropolis.es/files/File/Observatorio/Distritos/DossierZaragoza-marzo2018-Ebropolis.pdf
- Tezer H, Bedir Demirdağ TB. Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in children. Turk J Med Sci. 2020;50:592-603.
- Munro APS, Faust SN. Children are not COVID-19 super spreaders: time to go back to school. Arch Dis Child. 2020;105:618-9.
- Lee B, Raszka WV. COVID-19 Transmission and Children: The Child Is Not to Blame. Pediatrics. 2020;146:e2020004879.
- Posfay-Barbe KM, Wagner N, Gauthey M, Moussaoui D, Loevy N, Diana A, et al. COVID-19 in Children and the Dynamics of Infection in Families. Pediatrics. 2020;146:e20201576.