Vol. 17 - Num. 67
Notas clínicas
Estancamiento ponderal, vómitos y diarrea. Algo más que patología digestiva
María Romeo Donloa, C Aparicio Lópezb, C de Lucas Collantesb, MI Iglesias Bouzasc
aMIR-Pediatría. Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús. Madrid. España.
bServicio de Nefrología. Hospital Infantil Universitario Niño Jesús. Madrid. España.
cUnidad de Cuidados Intensivos Pediátricos. Hospital Universitario Niño Jesús. Madrid. España.
Correspondencia: M Romeo. Correo electrónico: maria3334@hotmail.com
Cómo citar este artículo: Romeo Donlo M, Aparicio López C, de Lucas Collantes C, Iglesias Bouzas MI. Estancamiento ponderal, vómitos y diarrea. Algo más que patología digestiva. Rev Pediatr Aten Primaria. 2015;17:247-50.
Publicado en Internet: 09-09-2015 - Número de visitas: 22888
Resumen
Las acidosis tubulares renales son un grupo de trastornos que cursan con acidosis metabólica, en las que la función glomerular permanece conservada y es la función tubular la que está alterada. Son producidas por un defecto en la reabsorción tubular renal de bicarbonato y/o en la excreción urinaria de ion hidrógeno. Su etiología es diversa. Se debe pensar en ellas ante un lactante con escasa ganancia ponderal, vómitos, poliuria y/o deshidratación. El pronóstico es variable, según corresponda a formas primarias o secundarias y a la rapidez con la que se instaure el tratamiento. Presentamos un paciente afecto de acidosis tubular distal primaria diagnosticado a los tres meses de edad, con clínica de estancamiento ponderal.
Palabras clave
● Acidosis tubular renal distal ● Estancamiento ponderal ● Nefrocalcinosis ● Orina alcalina ● VómitosINTRODUCCIÓN
La acidosis tubular renal es un síndrome clínico caracterizado por acidosis metabólica hiperclorémica debida a un defecto en la reabsorción tubular renal de bicarbonato y/o en la excreción urinaria de ion hidrógeno. La función glomerular es normal o está relativamente menos deteriorada que la función tubular1. Los síntomas de presentación en muchos casos son inespecíficos, por lo que se debe pensar en esta entidad para su diagnóstico precoz.
CASO CLÍNICO
Presentamos el caso de un lactante de tres meses de edad con historia de rechazo de tomas, náuseas, regurgitaciones y vómitos de un mes de evolución. Por este motivo fue derivado desde Atención Primaria al Servicio de Urgencias.
Fue un recién nacido a término de peso adecuado para la edad gestacional, con un embarazo de curso normal en el que no se objetivaron polihidramnios. El periodo neonatal cursó sin incidencias, presentando un desarrollo psicomotor y ponderoestatural adecuado hasta los dos meses de edad, cuando comenzó con la clínica descrita.
A su llegada a Urgencias, impresionaba de afectación del estado general, con mucosas secas, ojeroso, relleno capilar mayor de 2 segundos y palidez cutánea, con resto de la exploración física normal. Las constantes vitales fueron: temperatura, 36,6 °C; frecuencia cardiaca, 137 lpm; presión arterial; 88/55 mmHg (p75); saturación de O2, 100%; frecuencia respiratoria, 52 rpm; glucemia, 90 mg/dl. Peso de 5,995 kg (P10), talla de 60,5 cm (P10). Se expandió con suero fisiológico y se realizó analítica sanguínea (Tabla 1), con hemograma que fue normal y bioquímica en la que destacaba: Na 151 mEq/l; K 2,2 mEq/L; Cl 130 mEq/l y en la gasometría venosa: pH 7,29, pCO2 27 mmHg, bicarbonato 13 mmol/l y calcio iónico 1,74 mg/dl. Hallazgos compatibles con una acidosis metabólica con anion gap normal. Se realizó tira reactiva en orina de una micción con pH 7, densidad 1015 y resto negativo.
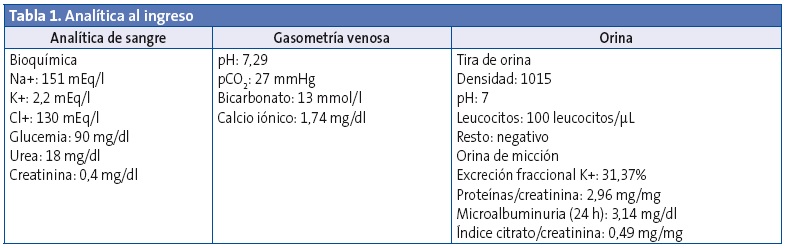
El paciente precisó sueroterapia intravenosa con aportes máximos de potasio (80 mEq/l) y bicarbonato (3 mEq/kg/día), y fue dado de alta en una semana, manteniendo tratamiento oral con bicarbonato sódico y citrato potásico. En la ecografía renal se objetivó hiperecogenicidad papilar bilateral, compatible con inicio de nefrocalcinosis. Se realizó valoración oftalmológica, serie ósea y potenciales auditivos, que fueron normales.
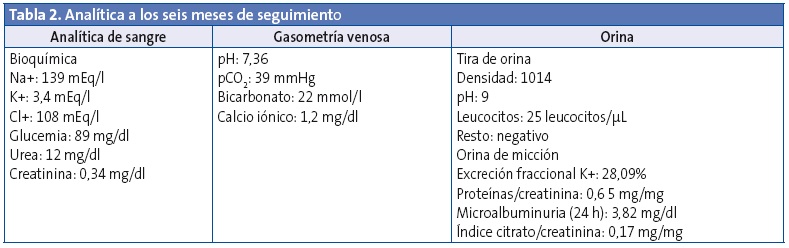
Durante el seguimiento hasta los nueve meses de edad el paciente se encuentra asintomático, con mejoría de su desarrollo ponderoestatural (p25 de peso y p50 de talla), por lo que se han ido realizando ajustes en las dosis de tratamiento en función del cambio de peso. La analítica a los seis meses del alta se recoge en la Tabla 2. En la ecografía de control realizada a los seis meses del alta persisten los hallazgos compatibles con nefrocalcinosis.
DISCUSIÓN
La pérdida de bicarbonato puede tener lugar a través del tracto gastrointestinal o del tracto urinario. En el caso que presentamos, se descartó el origen gastrointestinal y, dado que presentaba una acidosis metabólica con anion gap normal y un pH alcalino en orina, se sospechó el origen urinario de la misma.
La acidosis tubular proximal tipo II se debe a un defecto en la reabsorción tubular proximal de bicarbonato, caracterizada por una disminución del umbral renal para la excreción del mismo. La acidosis tubular distal tipo I se debe a un defecto en la capacidad de secreción de hidrogeniones por parte de las células α intercaladas del túbulo colector2. Cursa típicamente con una marcada hipopotasemia como compensación del gradiente electronegativo creado en la célula principal del túbulo al reabsorber sodio pero no cloro.
La acidosis distal tipo IV se produce por un defecto conjunto en la secreción tubular distal, tanto de hidrogeniones como de potasio; por lo tanto, cursa con hiperpotasemia.
El diagnóstico diferencial entre las diferentes acidosis tubulares se realiza mediante el cálculo del hiato aniónico en orina (Na+ + K+ - Cl-), que mide de forma indirecta la capacidad de síntesis de amonio; de manera que, si el resultado es negativo, el fallo es proximal, y si es positivo, es distal. El anion gap de nuestro paciente fue de +16,4, que corresponde a una acidosis tubular distal con hipopotasemia correspondiente a un tipo I3.
Ante un lactante con historia de escasa ganancia ponderal, vómitos, poliuria y/o deshidratación se debe descartar la presencia de acidosis metabólica mediante la realización de una gasometría venosa4,5. Además de realizar una tira reactiva de orina, ya que un pH alcalino orienta hacia una etiología renal de esa acidosis metabólica6,7.
En la historia clínica se deben recoger los antecedentes de consanguineidad, ya que algunos de estos trastornos corresponden a formas de herencia autosómica recesiva8.
Además de la evaluación de la función renal, se debe realizar una ecografía renal y una exploración a nivel auditivo y oftalmológico, ya que en ocasiones pueden formar parte de síndromes que asocien alteraciones a dichos niveles9.
El objetivo del tratamiento, mediante la corrección de la acidosis metabólica, es lograr un correcto desarrollo ponderoestatural y evitar las complicaciones de una acidosis crónica. La acidosis tubular tipo I suele precisar dosis entre 5-8 mEq/kg/día de solución alcalinizante, mientras que la proximal requiere dosis más elevadas debido a la disminución en el umbral renal de excreción de bicarbonato (10-20 mEq/kg/día)10.
CONCLUSIONES
En lactantes con estancamiento del desarrollo ponderoestural debemos considerar este posible diagnóstico, realizando gasometría venosa y tira reactiva de orina. Un pH alcalino persistente en orina en pacientes con acidosis sistémica debe hacer sospechar esta patología.
Las acidosis tubulares son entidades con un pronóstico muy variable, según correspondan a trastornos primarios o secundarios y la celeridad con la que se instaure el tratamiento.
CONFLICTO DE INTERESES
Los autores declaran no presentar conflictos de intereses en relación con la preparación y publicación de este artículo.
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
- García V, Luis M. Acidosis tubular renal. En: Antón M, Rodríguez ML. Nefrología pediátrica. Manual práctico. España: Editorial médica panamericana; 2011. p. 155-64.
- Escobar L, Mejía N, Gil H, Santos F. Distal renal tubular acidosis: a hereditary disease with an inadequate urinary H+ excretion. Nefrologia. 2013;33:289-96.
- Battle D, Hizon M, Cohen E, Gutterman C, Gupta R. The use of the urinary anion gap in the diagnosis of hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. N Engl J Med. 1988;318:594-9.
- Gil-Peña H, Mejía N, Santos F. Renal tubular acidosis. J Pediatr. 2014;164:691-8.
- Rodriguez Soriano J. Renal tubular acidosis: the clinical entity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2160-70.
- Ariceta G, Aguirre M. Tubulopatías. En: Protocolos Diagnóstico Terapéuticos de la AEP: Nefrología Pediátrica. 2.ª edición. Madrid: Ergón; 2008. p.137-46.
- Prieto JM, Franco, Mayor E, Palomino J, Prieto JF. Alteraciones del equilibrio ácido-base. Dial Traspl. 2012;33:25-34.
- Alper SL. Familiar renal tubular acidosis. J Nephrol. 2010;23:S57-76.
- Gil H, Santos F, García E, Álvarez MV, Ordóñez FA, Málaga S, et al. Distal RTA with nerve deafness: clinical spectrum and mutational analysis in five children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:825-8.
- Emmett M, Stern R, Forman JP. Etiology and diagnosis of distal (type 1) and proximal (type 2) renal tubular acidosis. En: UpToDate [en línea] [consultado el 09/09/2015]. Disponible en www.uptodate.com/contents/etiology-and-diagnosis-of-distal-type-1-and-proximal-type-2-renal-tubular-acidosis





